The guitar, with its timeless appeal and versatility, has captured the hearts of music enthusiasts for generations. Whether you’re a seasoned player or just starting on your musical journey, this ultimate guide to guitars will provide you with a wealth of knowledge, tips, and strategies to help you become a better guitarist.
step 1: Understanding Your Guitar
Before we dive into playing techniques and strategies, let’s start by getting to know your guitar inside out.
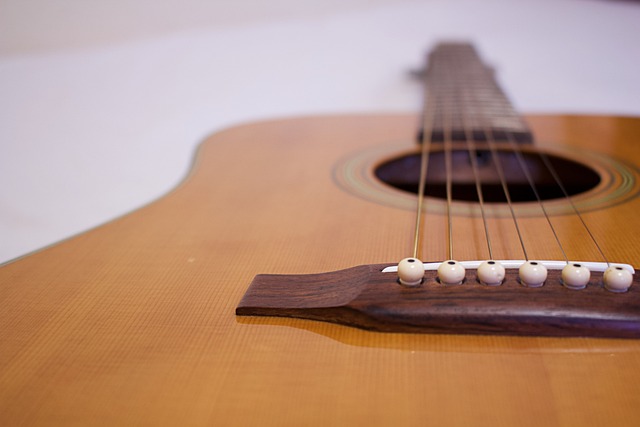
a. The Anatomy of a Guitar
Every guitarist should be familiar with the various components of their instrument. Here’s a quick overview:
Headstock: This is where the tuning pegs are located.
Nut: The nut is a small piece at the top of the fretboard, where the strings pass through.
Fretboard: The fretboard is the flat surface where you press the strings to create different notes.
Frets: Frets are the metal bars embedded in the fretboard that divide the neck into segments.
Neck: The neck is the long, narrow part of the guitar that houses the fretboard.
Body: The body of the guitar contains the sound hole (for acoustic guitars) or pickups (for electric guitars).
Bridge: The bridge holds the strings in place at the bottom end of the guitar.
b. Types of Guitars
Guitars come in various types, each with its own unique characteristics and tonal qualities. Some of the most common types include acoustic, classical, electric, and bass guitars. Understanding these differences is essential for selecting the right guitar for your style and preferences.
Step 2: Guitar Maintenance and Care
To keep your guitar in optimal playing condition, it’s crucial to perform regular maintenance. Here are some essential tips:
a. Cleaning Your Guitar
Use a clean, dry cloth to wipe down your guitar after each practice session.
For deeper cleaning, use a damp cloth and a mild guitar-specific cleaner.
Don’t forget to clean the fretboard and polish the frets.
b. Restringing Your Guitar
Change your strings regularly, as old strings can affect your guitar’s tone and playability.
Learn how to properly remove and replace strings, and always stretch new strings to minimize tuning issues.
c. Adjusting Your Guitar’s Action
Understand how to adjust the action (string height) to suit your playing style.
Consult a professional if you’re unsure about making these adjustments yourself.
d. Humidity and Temperature
Maintain the right humidity and temperature levels to prevent damage to your guitar.
Use a humidifier in dry conditions and a dehumidifier in overly humid environments.
Step 3: Guitar Playing Techniques
Now that you’re acquainted with your guitar and have learned how to take care of it, let’s explore various playing techniques.
a. Basic Chords
Master essential open chords like C, G, D, E, A, and F. These form the foundation of countless songs.
b. Strumming Patterns
Experiment with different strumming patterns to add rhythm and dynamics to your playing.
Practice various downstroke and upstroke patterns.
c. Fingerpicking
Learn fingerpicking techniques to create intricate melodies and accompaniments.
Start with simple patterns and gradually progress to more complex ones.
d. Barre Chords
Barre chords are moveable shapes that open up a world of chord possibilities. Mastering them can greatly expand your repertoire.
Step 4: Strategies for Guitar Improvement
To become a proficient guitarist, you need effective strategies for practice and skill development.
a. Practice Routine
Establish a consistent practice routine that includes warm-ups, technical exercises, and song learning.
Set achievable goals for each practice session.
b. Ear Training
Develop your ear by practicing interval recognition, chord progressions, and learning songs by ear.
Ear training enhances your ability to play by feel and improvise.
c. Music Theory
Invest time in understanding music theory concepts like scales, chords, and key signatures.
Music theory provides a solid foundation for composition and improvisation.
d. Recording and Feedback
Record your playing to analyze your performance objectively.
Seek feedback from experienced players or teachers to identify areas for improvement.
Step 5: Guitar Accessories
To enhance your playing experience, consider investing in useful guitar accessories:
a. Guitar Picks
Experiment with different pick materials and thicknesses to find your preferred choice.
b. Guitar Straps
A comfortable strap is essential for playing while standing.
c. Capos
Capos allow you to change the key of a song quickly.
d. Tuners
A reliable tuner is crucial for keeping your guitar in tune.
e. Guitar Cases
Protect your guitar during travel and storage with a sturdy case.
Step 6: Guitar Genres and Styles
The world of music is incredibly diverse, and the guitar plays a central role in many different genres and styles. Understanding these genres can broaden your horizons and inspire your playing.
a. Rock and Roll
History: Rock and roll emerged in the 1950s and is characterized by its energetic rhythms and prominent guitar work. Pioneers like Chuck Berry and Elvis Presley laid the foundation for this genre.
Techniques: To excel in rock and roll, focus on power chords, palm muting, and bending notes for that iconic rock sound.
b. Blues
History: Blues is all about expressing emotion through the guitar. Legendary players like Robert Johnson and B.B. King are known for their soulful blues guitar.
Techniques: Mastering techniques like slide guitar, string bending, and vibrato is essential for playing the blues.
c. Jazz
History: Jazz guitarists like Django Reinhardt and Wes Montgomery have shaped the genre with their complex chord voicings and improvisational skills.
Techniques: Jazz guitarists often use extended chords, arpeggios, and intricate picking patterns. Learning jazz standards and improvisation is key.
d. Classical
History: Classical guitar has a rich history dating back centuries. It’s characterized by fingerpicking and the use of nylon strings.
Techniques: Proper fingerstyle technique and reading sheet music are fundamental skills for classical guitarists.
e. Country
History: Country guitar is known for its twangy sound and storytelling quality. Legends like Chet Atkins and Johnny Cash are icons of this genre.
Techniques: Focus on chicken picking, pedal steel bends, and hybrid picking for an authentic country sound.
f. Metal
History: Metal guitarists like Jimi Hendrix and Eddie Van Halen pushed the boundaries of what the guitar could do, pioneering heavy riffs and virtuosic solos.
Techniques: Speed, precision, and knowledge of scales like the pentatonic and harmonic minor are crucial for metal guitarists.
Step 7: Guitar Gear and Equipment
a. Amplifiers
Having the right gear can significantly impact your sound and playing experience. Let’s explore some essential guitar equipment.
Amplifiers come in various types, including tube, solid-state, and modeling amps. Experimenting with different amps can help you find your signature sound.
b. Effects Pedals
Effects pedals, such as distortion, delay, and reverb, allow you to shape your tone and create unique sounds. Building a pedalboard is a fun aspect of being a guitarist.
c. Guitar Cables
High-quality cables are essential for a clear and noise-free signal. Invest in reliable cables to avoid technical issues during performances.
d. Guitar Maintenance Tools
Consider purchasing maintenance tools like a string winder, fretboard conditioner, and a setup kit to keep your guitar in top condition.
Step 8: Guitar Education and Resources
Continuing your guitar education is crucial for growth as a musician. Here are some educational resources to explore:
a. Online Guitar Lessons
Many websites and platforms offer comprehensive guitar lessons for all skill levels. Consider enrolling in structured online courses or tutorials.
b. Guitar Books
There are countless guitar books covering a wide range of topics, from theory to technique. Invest in a few authoritative books to expand your knowledge.
c. Guitar Teachers
Working with a guitar teacher or mentor can provide personalized guidance and feedback to help you reach your goals faster.
d. Online Communities
Join online guitar forums and communities to connect with other players, seek advice, and share your progress.
Step9: Your Guitar Journey
Your journey as a guitarist is unique, and it’s essential to enjoy every step along the way. Here are some final tips to keep in mind:
a. Patience and Persistence
Learning the guitar takes time, and progress may seem slow at times. Stay patient and persistent, and you’ll see improvement.
b. Set Goals
Set clear, achievable goals for your guitar playing. Whether it’s mastering a specific song or learning a new technique, having goals keeps you motivated.
c. Play with Others
Jamming with fellow musicians can be incredibly inspiring and enjoyable. Look for local music groups or join online collaborations.
d. Listen to a Variety of Music
Explore different genres and styles of music. You can learn valuable insights and techniques from various musical traditions.
e. Keep the Passion Alive
Remember why you started playing the guitar in the first place. The love for music and the instrument should always be your driving force.
As you embark on your guitar-playing journey, remember that progress takes time and dedication. Whether you aspire to become a professional guitarist or simply enjoy strumming your favourite tunes, the ultimate guide to guitars provides you with the knowledge, tips, and strategies to help you achieve your musical goals. So, pick up your guitar, start practicing, and let the music flow.
The guitar is a lifelong journey filled with discovery, creativity, and self-expression. This ultimate guide to guitars has equipped you with the knowledge, tips, and strategies to become a proficient and passionate guitarist. As you continue your musical adventure, embrace the challenges and joys of playing this incredible instrument. Your unique sound and style will contribute to the rich tapestry of guitar music for generations to come.
Happy playing and may your guitar always be your faithful companion on your musical journey! 🎸